Circle of Fifth
The circle of fifths is a way to represent the relationship between the 12 tones found in western music, as well as the alterations that each tone has. It is represented as a circle, like a clock, displaying tones instead of hours, with the C scale located on the “twelve” spot of a clock. Each tone is separated from the previous one, clockwise, in an interval of a fifth. If we go counter-clockwise, it is the interval of a fourth. Surprisingly, this kind of representation allows to classify the different scales by ascending number of alterations. If we go fifth by fifth (clockwise) the number of sharps increases. If you check on the previous image, C has no alterations, G has one sharp, D has 2 sharps… until reaching F# that has 6 sharps. On the contrary, if we go fourth by fourth (turning counter-clockwise), the number of flats increases.[…]
Read More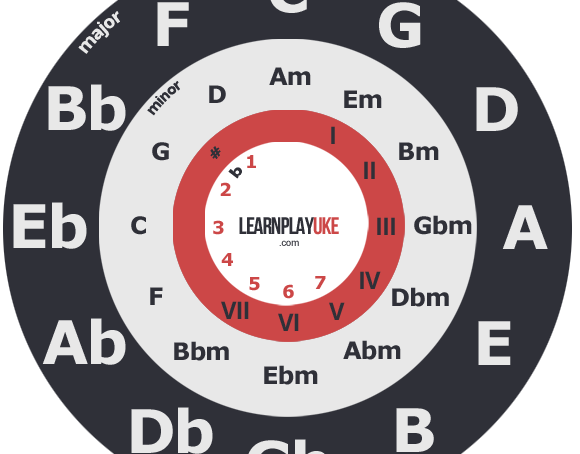


Sorry, your comment is incorrect. There can only be one letter note of each in a scale. ABCDEFG (whether they…